
Register with Plumtri!
Register on plumtri as an Individual or as an Organisation to gain access to all of its useful features and remain updated on the latest R&I news, events and funding opportunities.
-
 Welcome to plumtriA platform for Research & Innovation
Welcome to plumtriA platform for Research & Innovation -
 Looking for Funding?Check out the current open calls
Looking for Funding?Check out the current open calls -
 Register today to start receiving our monthly newsletter
Register today to start receiving our monthly newsletter -
 Looking to partner up?Search our list of registered profiles
Looking to partner up?Search our list of registered profiles -
 You have questions on a particular funding programme?
You have questions on a particular funding programme?
Project: MGMTOFGR - UM Study Investigates Promising Offshore Freshwater Reserves in East China Sea
Coastal regions and islands across the globe often face challenges in securing freshwater resources. In many coastal regions worldwide, there is a new and promising source of water called offshore freshened groundwater (OFG). This is fresh water stored in reservoirs that are below the ocean floor. A new study at the University of Malta has shed light on the existence of a potentially significant OFG system in the East China Sea, near the Shengsi Islands. The research, conducted by Prof. Aaron Micallef and Dr. Ariel T. Thomas from the Department of Geosciences, is the first numerical study of its kind in the East China Sea. The findings have been published in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Frontiers in Earth Science. This endeavour has been funded through the bilateral SINO-Malta Fund 2020 (Science and Technology Cooperation) managed by the Malta Council for Science and Technology (MCST) in Malta and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) in China.
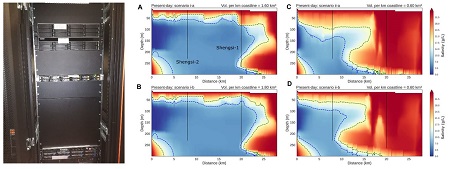
The study leveraged high-performance computing resources at the University of Malta to conduct a comprehensive numerical analysis. Dr. Thomas and the team created a 2D geological model of sub-seafloor sediments based on data gathered from previous studies. By simulating sea-level fluctuations over a span of the past 200,000 years, the researchers were able to examine the development of the freshwater system through time, and make some predictions about the present-day situation below the seafloor.The study's estimations suggest that the potential freshwater volume in the region could range from 0.5 to 1.6 km³, signifying a promising resource for the Shengsi region and the coastal metropolis of Shanghai. While these findings present an exciting prospect, the researchers emphasize the importance of further investigations employing geophysical techniques to deepen our understanding of this OFG system. This scientific achievement not only underscores the collaborative efforts between Malta and China through the SINOMALTA Fund but also paves the way for potential solutions to freshwater scarcity challenges in coastal regions.
Image description:
(left) AMD EPYC 7453 28-CORE High Performance Computer at the University of Malta.
(right) Numerical model results from Thomas et al (2023) showing different possible scenarios (A – D) of freshwater distribution below the seafloor. The blue dashed lines surround the regions of fresh groundwater, and the red represents the surrounding saline groundwater.
Read in more depth by clicking the below link.
