
Register with Plumtri!
Register on plumtri as an Individual or as an Organisation to gain access to all of its useful features and remain updated on the latest R&I news, events and funding opportunities.
-
 Welcome to plumtriA platform for Research & Innovation
Welcome to plumtriA platform for Research & Innovation -
 Looking for Funding?Check out the current open calls
Looking for Funding?Check out the current open calls -
 Register today to start receiving our monthly newsletter
Register today to start receiving our monthly newsletter -
 Looking to partner up?Search our list of registered profiles
Looking to partner up?Search our list of registered profiles -
 You have questions on a particular funding programme?
You have questions on a particular funding programme?
Vanishing Act for Water Waves
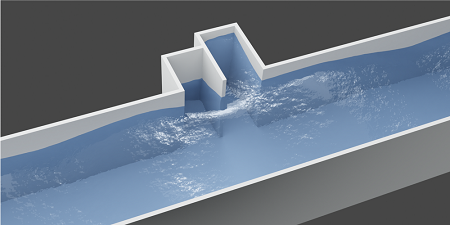
If waves of water, light, or sound were to impinge upon a hypothetical object called a perfect absorber, they would be neither reflected nor transmitted; they would simply vanish. Researchers have now demonstrated perfect absorption using ordinary water waves traveling down a narrow channel. The waves are canceled out by their own reflections from cavities built into the side of the channel. With further development, the researchers believe that the effect could be used to reduce erosion or protect sensitive structures by using an array of elements deployed near coastlines.
“We were motivated by the need to control or absorb waves in rivers or to protect coastlines,” says mathematical physicist Agnes Maurel of ESPCI Paris. “Completely absorbing wave energy is even better than redirecting it, and you can also imagine perhaps harvesting such energy.”
But achieving perfect absorption isn’t easy. Over the past few years, researchers working with waves of light or sound have demonstrated something very close to perfect absorption. But no one has created a perfect absorber for water waves.
Maurel and colleagues were inspired to try a new approach based on their own recent mathematical work, which showed that perfect absorption might be achieved by engineering a particular type of resonant structure with which incoming water waves would interact. This work showed that for waves traveling down a straight channel, these structures, when excited by a passing wave, would radiate secondary waves that would perfectly cancel the waves going both forward and backward.
To demonstrate this theory in practice, Maurel and her colleagues followed a two-stage procedure: first they analyzed how cavities can produce zero transmission at particular frequencies, and then they fine tuned that setup to produce zero reflection at those same frequencies. They considered a water channel 1.4 m long, 6 cm wide, and 5 cm deep. In preliminary calculations starting from the equations for an ideal fluid—one having no energy losses due to friction—they showed that two small cavities built into the side of the channel could act as the required resonant chambers. These calculations assumed that the two cavities were of identical size, extending away from the channel wall by 4 cm and extending along the channel for 3 cm. For waves in the frequency range that the team studied, these calculations predicted zero transmission at 2.7 and 3.3 Hz.
The team then tested these predictions with water waves in the lab. In close correspondence with the predictions, the researchers found two dips in the transmission-vs-frequency curve—the first very nearly going to zero and the second dipping to about 40%. The discrepancies with theory, the researchers say, reflect the friction losses in the fluid and the approximations employed in the analysis.
Continue reading the full article by clicking on the below link.
